When it comes to cloud computing, you'll be grappling with the question of "who's the right cloud provider for you." Both cloud ecosystems offer myriad benefits, from superior computing power, scalability and security to unmatched cost efficiency and carbon footprint reduction. The cloud computing industry has evolved rapidly and today presents a vast array of cloud providers, technologies, products and services. Comparison is often not easy, as cloud providers use many technical terms for similar offerings. The same technology has different names, making it difficult to compare similar features. In this blog, we take a close look at AWS and AZURE for you and compare these two cloud providers on their offerings.
Amazon Web Service and Microsoft AZURE
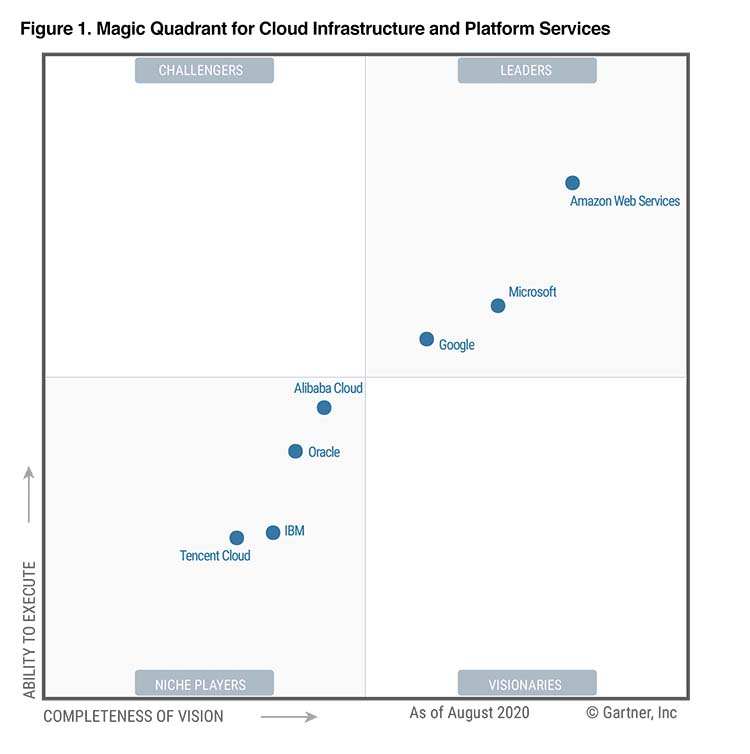
Every industry has its leaders - a few companies that stand out from the rest and set the standard for excellence. Besides the two cloud providers compared here, there are of course other cloud product and service providers in the market such as; Google Cloud Platform, IBM, Alibaba Cloud.
With its launch in 2006, AWS is the oldest cloud provider in the market. Google followed shortly after, in 2008. With these years of experience, the two companies are known for their innovation, excellence and market dominance. As pioneers in this industry, they had the ideal technology foundation, expertise and financial resources to develop industry-leading cloud computing platforms.
Also in Gartner's Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services, Microsoft AZURE and Amazon Web Services are again ranked first and second as market-leading cloud providers. Both are in the top right corner of the Leaders quadrant, awarded for ability to execute and completeness of vision. AWS takes the honor of first place, securing the top spot for the tenth year in a row.
Amazon Web Services vs. Microsoft Azure feature comparison
Commonalities
In terms of standard functions for building cloud structures, AWS and Azure are similar. Both provide virtual computing, networking, databases and other cloud functions. Likewise, both are continuously working on expanding the range of services or optimizing existing functions. Both portals are managed via the respective web portals and CLIs. To use AWS and Azure successfully, you need a corresponding expert who sets the course for the cloud project, accompanies the migration and looks after the infrastructure accordingly.
Differences
AWS customers benefit from a global infrastructure and flexible cost billing (pay as you go). The strengths of AWS lie in the flexible design of AWS resources. Server instances, for example, can be scaled upwards without any problems if the accesses to the web application increase.
Amazon Web Services can deal optimally with Linux in particular. Of course, it is also possible to work with Windows in AWS. Further assistance is provided by the Windows Study Guide, among others.
Azure relies on hybrid technologies. This means that almost all functions can be connected to local data centers. Of course, other Microsoft products (such as Exchange, SharePoint, SQL Server, Office 365) can be integrated into the Azure cloud. Azure focus is on Windows, but of course Linux is also supported. Azure's pricing model is more inflexible compared to AWS. Microsoft is also global, but it is still much more complex to secure workloads across multiple regions.
As traditional systems have moved from on-premises to the cloud, both vendors have expanded their service offerings to include more than 25 different cloud solution categories. There is a wide range of categories that include computing power, storage, databases, security, robotics, machine learning and even quantum technologies.
Compute functions
Compute functions or compute resource are the foundation on which the cloud environment is built. Therefore, the decision in this category is very important. As it has a direct impact on the speed and performance of your platform.
When comparing the compute capacities of Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure, we compare the technology offering in terms of virtual machines (VMs). VMs are the foundation of the cloud environment and emulate the functionality of physical computing systems to handle almost any workload imaginable. Both AWS and Azure take a similar approach to VMs. Amazon Web Services compute offering is known as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2). Microsoft, on the other hand, refers to its compute product as Azure Virtual Machines.
Virtual machine features
- The ability to use stored disk images to create instances
- On-demand capabilities to start and stop instances
- Restriction-free management of your instances
- The ability to tag your instances
- A variety of available operating systems to install on your instance
- Access to virtual machines
- You'll find that both Azure and AWS take a similar approach to VM access for Linux and Windows machines.
For Linux machines, if you need SSH-based terminal access, both Amazon EC2 and Azure require that a custom SSH key be inserted. In addition, neither vendor supports SSH browser access.
When providing additional access paths, the two cloud providers are easier to differentiate. AZURE provides additional access to Windows machines via Microsoft PowerShell, while Amazon EC2 provides additional access to Windows machines via its IPv6 address and Session Manager.
Virtual machine instance types
To simplify and speed up the process of deploying a VM setup, both Azure and Amazon EC2 offer a wide range of predefined instances. Each VM instance type is configured with a specific virtual CPU, RAM and networking components.
Both vendors build flexibility into the process and allow you to customize individual configurations. You can reconfigure core elements of the predefined instance, including the number of CPUs and available RAM, which opens up the ability to scale VM resources up or down to meet unique business needs. Both vendors offer extremely high-end specifications to support the most demanding workloads. They currently max out with the following specifications:
- Amazon EC2 VMs scale up to 448 vCPUs and 24,576 GB of RAM.
- Microsoft Azure VMs scale up to 416 vCPUs and 11,400 GB of RAM.
To further simplify the process, both vendors group VM types into categories that are optimized and configured for their intended use. These VM categorizations include general-purpose, memory-optimized, compute-optimized, memory-optimized, graphics processing (GPU) and high-performance.
Automatic scaling of virtual machine instances
Auto-scaling allows you to create and remove VM instances in accordance with user-defined policies. You can optimize performance and scale compute resources up or down in real time to meet demand. This helps control costs by minimizing unused resources and paying only for what is actually needed.
Both Amazon EC2 and Azure support autoscaling and implement it in a similar way:
- AWS Auto Scaling scales instances into groups. Each group has a starting configuration to create new instances and uses your chosen scaling plan to manage the creation and removal of instances.
- Azure Autoscale has a VM scaling set in which instances are scaled. Instances are created or removed in accordance with your chosen scaling plan, which is called an Autoscale policy.
Network capabilities
Azure and AWS cloud platforms are built on global cloud infrastructure with hundreds of data centers connected by hundreds of thousands of lit fiber and submarine cable systems. Both are known for delivering state-of-the-art network services that provide high-speed performance, high availability, strong security, and global coverage.
Amazon Web Service
AWS has the most extensive global cloud infrastructure. No other cloud provider offers as many regions and Availability Zones, all featuring low latency, high throughput, and a highly redundant network. AWS is available in 81 Availability Zones within 25 geographic regions worldwide. In addition, 21 more Availability Zones and 7 more AWS regions are planned in Australia, India, Indonesia, Israel, Spain, Switzerland and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The AWS Regions and Availability Zones model is recommended by Gartner as a proven approach for running enterprise applications that require high availability.
Microsoft AZURE
The Azure cloud platform consists of more than 200 products and cloud services. Microsoft AZURE has cloud network locations in more than 60 regions and is available with 170 network points of presence (PoP) worldwide. The global Azure infrastructure consists of two main components: the physical infrastructure and the networking components for networking. The physical component includes at least 200 physical data centers arranged in regions and connected by one of the largest networks in the world. Thanks to the connectivity of the Azure global network, all Azure data centers each offer high availability, low latency, scalability and the latest in cloud infrastructure - all united on the Azure Platform.
Microsoft also has ambitious expansion plans for its global Azure network. Plans for new Microsoft data centers include Austria, Chile, Denmark, Greece, Israel, Italy, Mexico, New Zealand, Poland, Qatar, Spain, Sweden, Taiwan and the U.S. (Arizona).
Billing and pricing
Comparing prices between cloud providers is one of the most difficult aspects of the decision process.
AWS vs. Azure cloud price comparison
Both AWS and Azure offer you a variety of choices from hundreds of comparable cloud products and services.
Each provider offers its own unique pricing mechanism and set of configurable options that affect the overall cost. Even for a simple cloud installation of a single VM instance with attached storage, you have thousands of product configurations and pricing options to choose from.
Cloud Price Calculator
To provide an accurate price comparison, both Amazon and Microsoft have created comprehensive cloud price calculators that give you each product, configurable option and associated price.
Pay-As-You-Go
Pay-as-you-go pricing offers a flexible, on-demand approach to cloud resource consumption. Ideal for organizations with irregular cloud usage, this option allows cloud resources to be added and removed as needed. However, this flexibility comes at a price, with pay-as-you-go pricing models having the highest price per hour:
Instance type | Amazon EC2 | AWS Price(per hour) | Azure VM | Azure Price(per hour) |
General purpose | t4g.xlarge | $0.134 | B4MS | $0.166 |
Computer optimized | c6g.xlarge | $0.136 | F4 | $0.199 |
Memory optimized | r6g.xlarge | $0.201 | E4a v4 | $0.252 |
When comparing prices for AWS and Azure VMs, Amazon EC2 is the clear winner for general purpose instance types, compute optimized instances, and storage optimized instances. AWS is at least 20% cheaper in all three categories.
Summary
In the comparison between Amazon Web Services and Azure, AWS is the clear winner. In summary, the key factors in this decision can be attributed to the following aspects;
- AWS was consistently hailed as a leader in Gartner's Magic Quadrant.
- Industry-wide research shows that Amazon has a larger cloud market share than Azure
- AWS offers more cloud products and services than Azure does
- Amazon's cloud network is larger, with more points of presence around the world
- AWS beats Azure across the board in Cockroach Labs' independent research on compute, networking and storage performance
- AWS is cheaper than Azure when it comes to the compute power that forms the backbone of cloud deployments.
In the end, which provider is best depends on the project at hand. If extreme load scenarios are expected, then AWS is the best choice. Azure is recommended if the workloads are primarily Microsoft-based or if existing Microsoft applications are to be supplemented with the cloud component. In these cases, customers get Azure capacity for free. For this reason, many companies use Azure as a second cloud platform alongside AWS and thus rely on a multi-cloud strategy.
Both providers allow a free trial of their offerings with different specifications:
AWS | AZURE |
AWS Azure As part of a 12-month free tier account, the service offering (restricted - Free Tier Services) can be tried out. | Offers a free trial period of 30 days, during which one can test all available resources within a cost limit of 170€. |